
At this point HTML and HTTP had already been in development for about two months and the first Web server was about a month from completing its first successful test. With help from his colleague and fellow hypertext enthusiast Robert Cailliau he published a more formal proposal on 12 November 1990 to build a "Hypertext project" called "WorldWideWeb" (one word, abbreviated 'W3') as a "web" of "hypertext documents" to be viewed by " browsers" using a client–server architecture. There is no reason, the proposal continues, why such hypertext links could not encompass multimedia documents including graphics, speech and video, so that Berners-Lee goes on to use the term hypermedia.
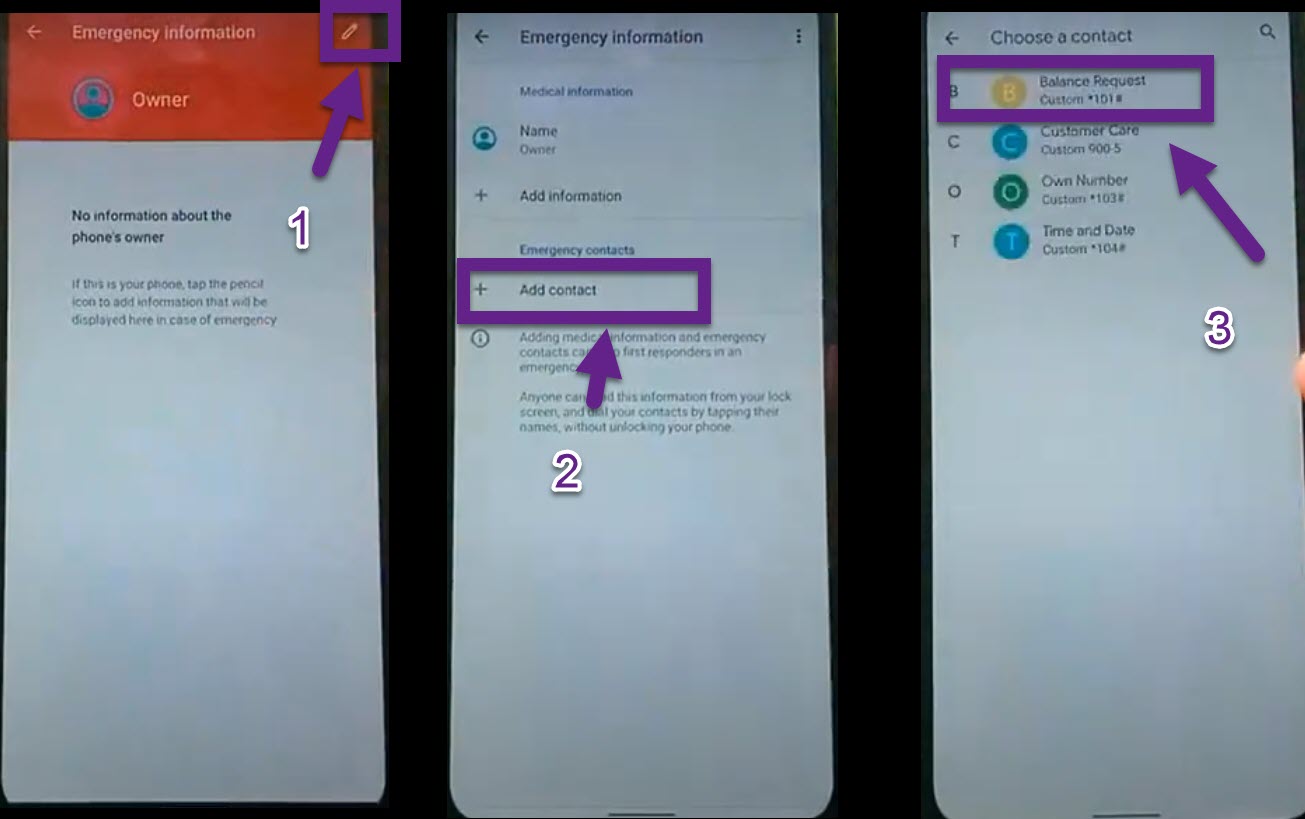
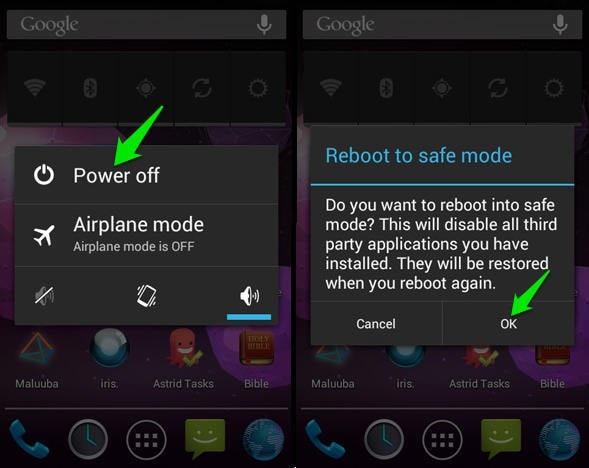
#Pattern password disable youtube software
On 12 March 1989, he submitted a memorandum, titled "Information Management: A Proposal", to the management at CERN for a system called "Mesh" that referenced ENQUIRE, a database and software project he had built in 1980, which used the term "web" and described a more elaborate information management system based on links embedded as text: "Imagine, then, the references in this document all being associated with the network address of the thing to which they referred, so that while reading this document, you could skip to them with a click of the mouse." Such a system, he explained, could be referred to using one of the existing meanings of the word hypertext, a term that he says was coined in the 1950s. While working at CERN, Berners-Lee became frustrated with the inefficiencies and difficulties posed by finding information stored on different computers. In 1988 the first direct IP connection between Europe and North America was made and Berners-Lee began to openly discuss the possibility of a web-like system at CERN. By 1985, the global Internet began to proliferate in Europe and the Domain Name System (upon which the Uniform Resource Locator is built) came into being. Tim Berners-Lee's vision of a global hyperlinked information system became a possibility by the second half of the 1980s. Both Nelson and Engelbart were in turn inspired by Vannevar Bush's microfilm-based memex, which was described in the 1945 essay " As We May Think". The corridor where The underlying concept of hypertext originated in previous projects from the 1960s, such as the Hypertext Editing System (HES) at Brown University, Ted Nelson's Project Xanadu, and Douglas Engelbart's oN-Line System (NLS). Websites are provided for a myriad of informative, entertainment, commercial, and governmental reasons. Website content can be provided by a publisher, or interactively from user-generated content. Websites are stored in computers that are running a web server, which is a program that responds to requests made over the Internet from web browsers running on a user's computer. Multiple web resources with a common theme and usually a common domain name make up a website. In addition to text, web pages may contain references to images, video, audio, and software components which are either displayed or internally executed in the user's web browser to render pages or streams of multimedia content. Special HTML syntax displays embedded hyperlinks with URLs which permits users to navigate to other web resources. Web resources may be any type of downloaded media, but web pages are hypertext documents formatted in Hypertext Markup Language (HTML). The World Wide Web has been central to the development of the Information Age, and is the primary tool billions of people use to interact on the Internet. The Web began to enter everyday use in 1993–4, when websites for general use started to become available. The browser was released outside CERN to other research institutions starting in January 1991, and then to the general public in August 1991. He wrote the first web browser in 1990 while employed at CERN near Geneva, Switzerland. The World Wide Web ( The World Wide Web is not synonymous with the Internet, which pre-dated the Web in some form by over two decades and upon the technologies of which the Web is built.Įnglish scientist Tim Berners-Lee invented the World Wide Web in 1989. A global map of the Web Index for countries in 2014


 0 kommentar(er)
0 kommentar(er)
